1. What is a journal entry? Give an example.
Ans. A journal entry is a record of a financial transaction in chronological order. It is used to record the details of a transaction, such as the date of the transaction, the accounts involved, and the amounts debited or credited. Journal entries are used as the basis for preparing other financial statements, such as the general ledger, trial balance, and financial statements.
Here's an example of a journal entry:
Date: January 1, 2023
Account debited: Cash
Amount: 10,000
Account credited: Sales
Amount: 10,000
In this example, the transaction is a sale of a product for 10,000. The Cash account is debited by 10,000, which represents the amount received in cash from the sale. The Sales account is credited 10,000, which represents the amount of the sale.
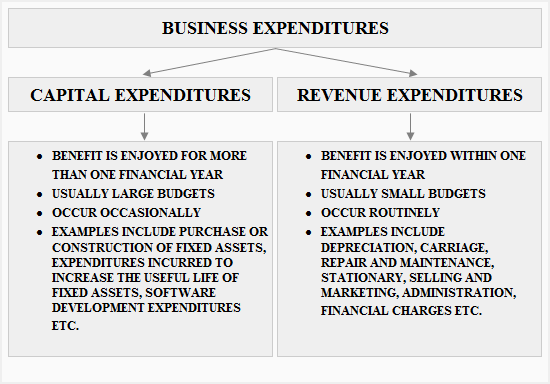
2. Explain the difference between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure.
Ans. Capital Expenditure refers to the cost of acquiring a fixed asset or making improvements to an existing fixed asset. These expenditures are made to generate long-term benefits for the business. Examples of capital expenditures include the purchase of land, buildings, machinery, and equipment.
Revenue Expenditure, on the other hand, refers to the cost of running a business on a day-to-day basis. These expenditures are made to maintain the business and generate revenue in the short term. Examples of revenue expenditures include salaries, rent, utilities, and advertising.
The main difference between the two is that Capital Expenditure is a long-term investment that is expected to generate benefits over several years, while Revenue Expenditure is a short-term expense that is necessary to keep the business running daily.
3. What is goodwill? How is it calculated?
Ans. Goodwill is an intangible asset that represents the value of a company's brand, reputation, and customer relationships. It is calculated by subtracting the net assets of the company from the purchase price of the company.
The formula to calculate goodwill is as follows:
Goodwill = Purchase Price - Net Assets
Here, the purchase price refers to the amount paid to acquire the company, and the net assets refer to the total assets of the company minus the total liabilities.
For example, if a company is acquired for a purchase price of 500,000 and has net assets of 300,000, then the goodwill will be:
Goodwill = 500,000 - 300,000
Goodwill = 200,000
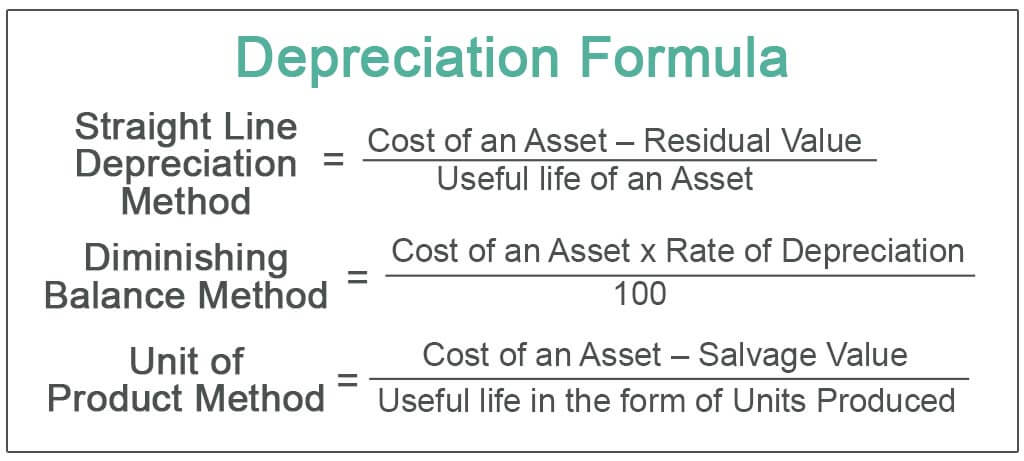
4. Define Depreciation. What are the different methods of calculating depreciation?
Depreciation is the reduction in the value of a fixed asset over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or other factors. It is a non-cash expense that is charged against the income of the business to reflect the decline in the value of the asset.
There are several methods of calculating depreciation, including:
a. Straight-line method: This method calculates depreciation by dividing the cost of the asset by its useful life. The same amount of depreciation is charged every year.
b. Diminishing balance method: This method calculates depreciation as a percentage of the remaining book value of the asset. The percentage is usually higher in the early years and decreases over time.
c. Annuity method: This method calculates depreciation as a fixed amount each year, based on the total cost of the asset and its useful life.
5. What is Trial Balance and what is its purpose?
Ans. A trial Balance is a list of all the ledger balances of a company's accounts. It is used to ensure that the total debits of all accounts equal the total credits of all accounts, and it is prepared to ensure the accuracy of the accounting records. The purpose of the trial balance is to detect any errors that may have occurred during the recording of transactions. If the total debits and credits are not equal, it indicates that there is an error in the accounting records, and the errors must be located and corrected.
6. What is a Balance Sheet? Explain its components.
Ans. A Balance Sheet is a financial statement that shows the company's financial position at a particular point in time. It reports the company's assets, liabilities, and equity. The balance sheet components are:
a. Assets: Assets are the resources owned by the company, which are expected to provide future economic benefits. Assets can be classified into current and non-current assets. Current assets are those that can be converted into cash within a year, while non-current assets are those that are expected to provide benefits beyond a year. Examples of assets include cash, inventory, property, plant, and equipment.
b. Liabilities: Liabilities are the obligations owed by the company to its creditors or lenders. Liabilities can be classified into current and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are those that are due within a year, while non-current liabilities are those that are due beyond a year. Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, loans, and bonds payable.
c. Equity: Equity is the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities. Equity can be classified into capital and retained earnings. Capital represents the investment made by the owners of the company, while retained earnings represent the accumulated profits of the company that have not been distributed to the owners.
7. Define the Cash Flow Statement. What are its components?
A cash Flow Statement is a financial statement that shows the inflow and outflow of cash during a particular period. It reports the sources and uses of cash and helps in determining the company's ability to generate cash. The components of the cash flow statement are:
a. Cash flow from operating activities: This section reports the cash inflows and outflows from the company's operating activities, such as sales and expenses.
b. Cash flow from investing activities: This section reports the cash inflows and outflows from the company's investing activities, such as the purchase or sale of fixed assets.
c. Cash flow from financing activities: This section reports the cash inflows and outflows from the company's financing activities, such as the issue of shares or payment of dividends.
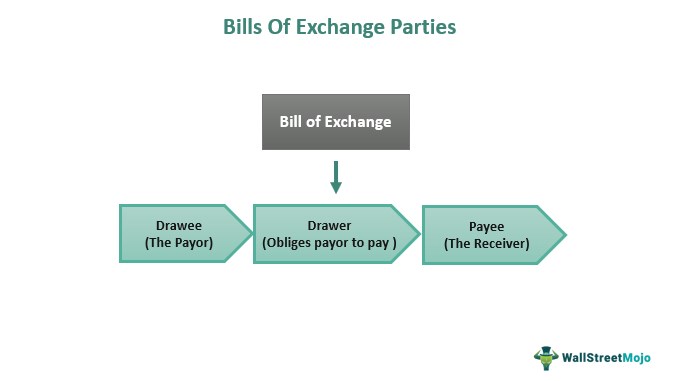
8. What is a Bill of Exchange? Explain its types.
A Bill of Exchange is a written instrument that contains an order to pay a specified amount of money to a specified person or entity. It is a negotiable instrument and can be transferred from one person to another. The types of Bill of Exchange are:
a. Trade Bill: A trade bill is a bill of exchange that arises out of a commercial transaction, such as the sale of goods.
b. Accommodation Bill: An accommodation bill is a bill of exchange that is created to lend money to the acceptor.
c. Banker's Acceptance: A banker's acceptance is a bill of exchange that is accepted by a bank, which is a guarantee of payment.
9. What is Partnership? Explain its features.
Ans. A partnership is a type of business organization in which two or more people come together to carry on a business to profit. The features of partnership are:
a. Agreement: A partnership must have a partnership agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of the partnership, including the rights and obligations of each partner.
b. Number of partners: A partnership must have at least two partners and can have up to twenty partners in the case of a general partnership, and up to fifty partners in the case of a banking business.
c. Profit sharing: Partners share the profits and losses of the business according to the partnership agreement. The sharing can be in equal proportions or proportion to the capital contribution made by each partner.
d. Unlimited liability: Partners have unlimited liability for the debts and obligations of the partnership. This means that each partner is personally liable for the debts and obligations of the partnership.
e. Mutual agency: Partners are agents of the partnership and can act on behalf of the partnership. Each partner can bind the partnership to a contract or agreement, and the actions of one partner are binding on all partners.
10. What is Goodwill? Explain its types.
Goodwill is the value of a business that is over and above the value of its tangible assets. It is an intangible asset that arises when a business has a favorable reputation, customer base, or other intangible assets that contribute to its earning capacity.
The types of Goodwill are:
a. Purchased Goodwill: Purchased goodwill is the goodwill that arises when a company acquires another company for a price that is higher than the fair market value of the net assets of the acquired company.
b. Self-generated Goodwill: Self-generated goodwill is the goodwill that arises when a company establishes a favorable reputation, customer base, or other intangible assets through its efforts.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Goodwill-Definition-6b68b9485c394cb185b3097a8558a25e.jpg)



0 Comments